Imagine having a personal AI assistant that can answer questions about specific documents or knowledge bases while remembering your entire conversation history. This project demonstrates exactly that by implementing a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system deployed on Kubernetes that combines the power of large language models with your own data.
In this article, we'll explore how this system works by breaking down each component in simple terms. By the end of this guide, you'll understand how to build your own intelligent conversational agent that can work with any type of document or knowledge base. The full code can be found in this Github repository.
1. What is RAG and Why Does It Matter?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that enhances AI chatbots by giving them access to specific information beyond their training data. Traditional AI models are limited to the information they learned during their training process, which means they can't access real-time information or answer questions about documents they've never seen before.
A RAG system works by first searching through your documents to find relevant information, then retrieving the most relevant pieces of text, and finally generating responses using both the retrieved information and the AI's existing knowledge. This approach solves the critical problem of knowledge cutoffs and enables AI systems to work with domain-specific information that wasn't part of their original training data.
The power of RAG lies in its ability to make AI systems more accurate, up-to-date, and relevant to specific use cases. Instead of hallucinating or providing outdated information, the AI can reference actual documents and provide citations for its responses.
2. System Architecture Overview
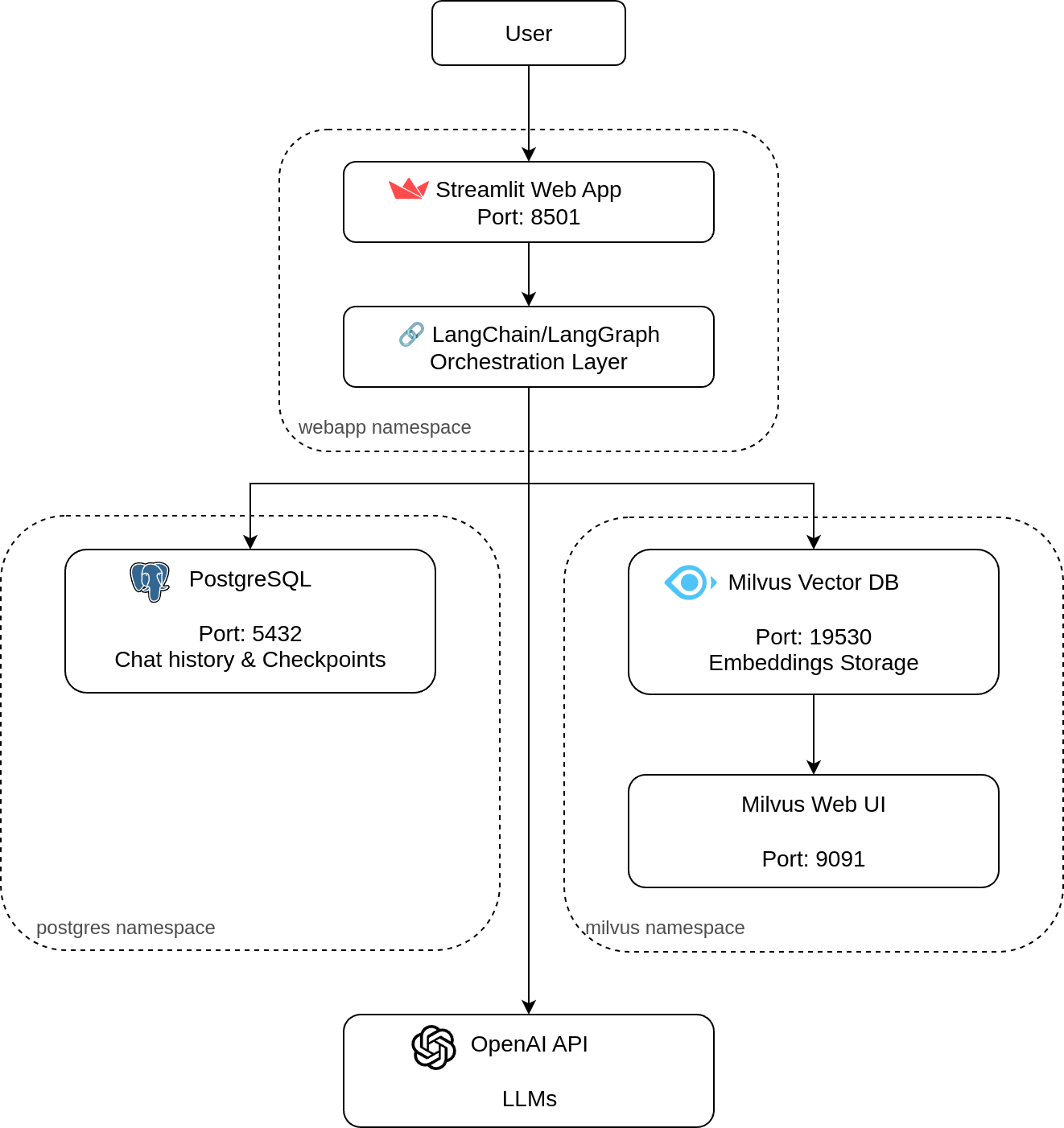
Our RAG system consists of several key components working together in a coordinated workflow. When a user submits a question through the Streamlit web application, the request flows through a LangGraph RAG chain that intelligently decides whether to search the vector database for relevant information. The system then combines any retrieved information with the conversation context stored in PostgreSQL before sending everything to the OpenAI GPT model for final response generation.
This architecture ensures that every response is both contextually aware of the ongoing conversation and informed by the most relevant information from your document collection. The entire system runs on Kubernetes, providing scalability, reliability, and easy management of all components.
3. Component Breakdown
3.1 LangChain & LangGraph - The AI Orchestration
LangChain serves as the foundation for building applications with large language models, while LangGraph extends these capabilities to create stateful, multi-step AI workflows. Together, they form the brain of our RAG system, orchestrating the complex dance between user input, information retrieval, and response generation.
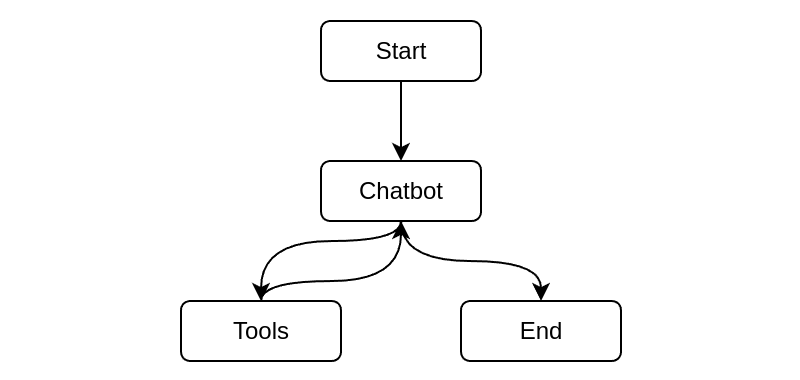
The core logic of the graph is described in the figure above. The system works by receiving user questions and making intelligent decisions about how to respond.
- For simple queries that don't require additional context, the system might respond directly using the AI's existing knowledge (right path).
- However, for questions that would benefit from specific information, LangGraph may decide to use the tools (left path) that you have provided to gather extra information: for example, that could be a tool that executes online searches or a tool that retrieves relevant documents from an internal database. Once relevant information is retrieved, LangGraph coordinates the combination of this context with the user's original question and the ongoing conversation history, and decides whether to use another tool or to prepare a response. This orchestration ensures that responses are not only accurate based on the retrieved information but also coherent within the context of the entire conversation thread.
3.2 OpenAI GPT - The Language Model
The OpenAI GPT model serves as the core intelligence of our system, providing natural language understanding and generation capabilities that make conversations feel human-like and intuitive. The language model performs multiple critical functions within our system.
- First, it analyzes incoming user questions to determine whether additional information retrieval is necessary or if the question can be answered directly from the model's existing knowledge. This decision-making capability prevents unnecessary tool usage and improves response times for simple queries.
- In addition, when the system retrieves relevant information after using one of the tools, the GPT model synthesizes this information with the conversation context to generate comprehensive, coherent responses.
3.3 Milvus - The Vector Database
Milvus represents a specialized database technology designed specifically for storing and searching through vector embeddings, which are numerical representations of text that capture semantic meaning. This component transforms how we search and retrieve information, moving beyond simple keyword matching to true semantic understanding.
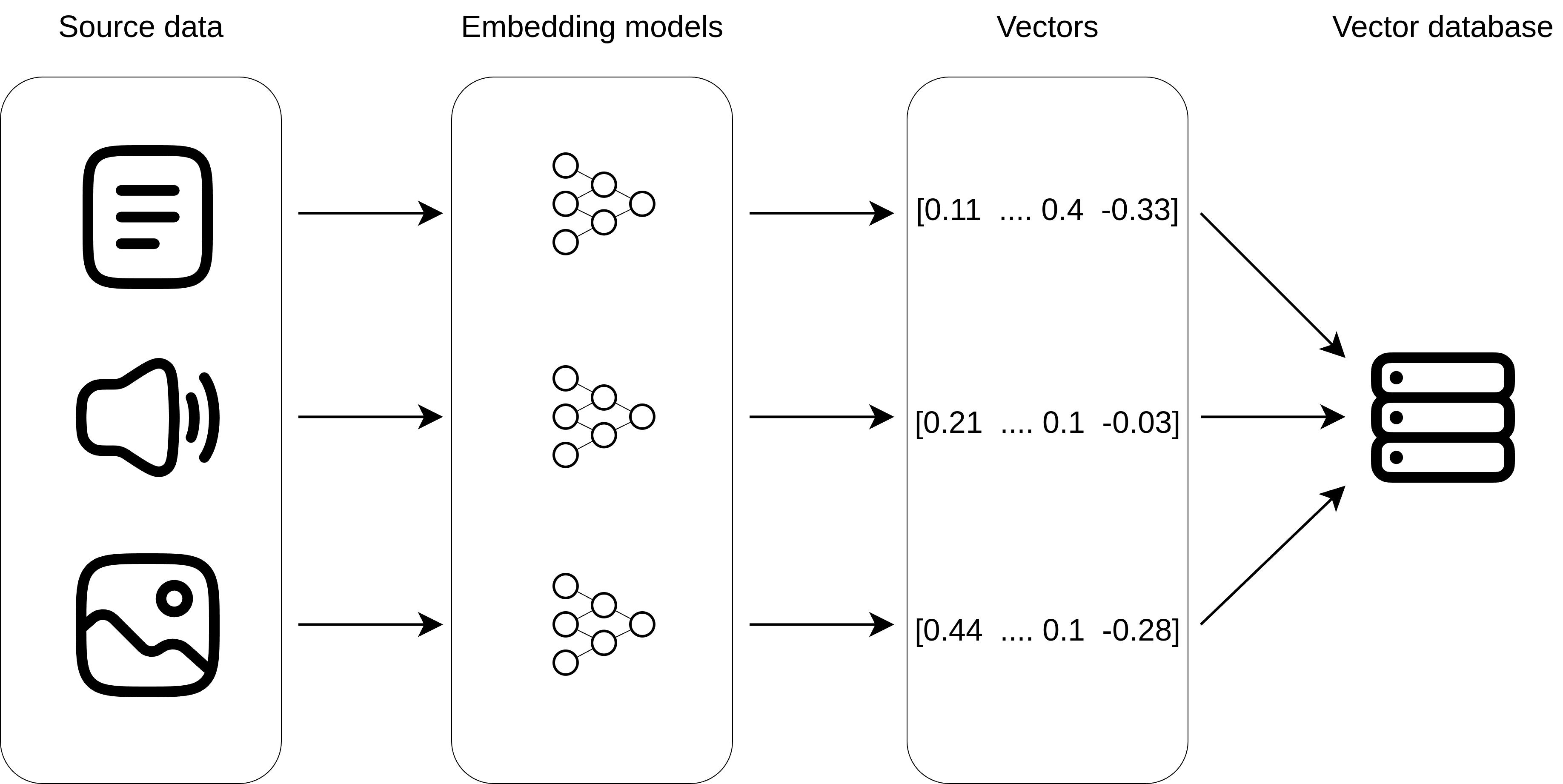
The process begins when documents are processed and split into manageable chunks, typically a few hundred words each. Each chunk is then converted into a high-dimensional vector using OpenAI's embedding model, which captures the semantic meaning of the text in mathematical form. These embeddings are stored in Milvus along with the original text and relevant metadata.
When a user asks a question, the system converts their query into the same type of vector embedding and searches through the database to find the most semantically similar content. This approach enables the system to find relevant information even when the exact words don't match. For example, a search for "car problems" might successfully return documents about "automotive issues" or "vehicle maintenance" because the vector representations capture the underlying semantic relationships.
The sophistication of vector-based search cannot be overstated. Traditional keyword searches often miss relevant information due to variations in terminology, but vector search understands context and meaning, dramatically improving the quality of information retrieval.
3.4 PostgreSQL - The Memory System
PostgreSQL serves as the memory backbone of our conversational AI system, storing conversation history and checkpoints that enable the AI to maintain context across multiple interactions. This database management system ensures that each conversation thread maintains continuity and coherence, regardless of how long the interaction continues.
The importance of persistent memory in conversational AI cannot be understated. Without proper memory management, each interaction would be isolated, forcing users to repeatedly provide context and preventing the development of more sophisticated, multi-turn conversations that feel natural and productive.
3.5 Streamlit - The User Interface
Streamlit serves as the user-facing component of our system, providing a clean and intuitive web interface for interacting with the AI assistant. This Python framework allows developers to create sophisticated web applications without extensive web development knowledge, making it an ideal choice for data science and AI applications. The biggest advantage of streamlit is the easy management of different user sessions: you can open two tabs of the same application, start two different conversations, and there will be no information leak between them.
3.6 Kubernetes - The Deployment Platform
Kubernetes orchestrates the deployment and management of all system components, providing a robust platform that handles scaling, reliability, and inter-service communication. This container orchestration platform ensures that our RAG system can operate reliably in production environments while maintaining the flexibility to scale based on demand.
Each component of our system runs in its own containerized environment, managed by Kubernetes. This approach provides isolation between services, making the system more resilient to failures and easier to maintain. If one component experiences issues, the others continue operating normally, and Kubernetes can automatically restart failed services to maintain system availability.
The platform also manages networking between components, ensuring secure communication channels and proper service discovery. When the Streamlit application needs to communicate with the vector database or the PostgreSQL instance, Kubernetes handles the routing and load balancing automatically. This infrastructure management allows developers to focus on application logic rather than deployment complexities.
For organizations planning to scale their RAG systems, Kubernetes provides horizontal scaling capabilities that can automatically add more resources during peak usage periods and scale down during quieter times. This elasticity ensures optimal performance while controlling infrastructure costs.
4. How Everything Works Together
Understanding the complete workflow helps illustrate how these components create a cohesive, intelligent system. When a user submits a question through the Streamlit interface, the application immediately saves this interaction to the conversation history and forwards the query to the LangGraph workflow engine.
LangGraph analyzes the incoming question using the OpenAI language model to determine the appropriate response strategy. For questions that clearly require specific information not available in the model's training data, the system triggers its retrieval mechanism. This involves converting the user's question into a vector embedding and searching the Milvus database for semantically similar content.
The vector database returns the most relevant document chunks, which LangGraph then combines with the original user question and the complete conversation history stored in PostgreSQL. This comprehensive context package is sent to the OpenAI GPT model, which synthesizes all available information into a coherent, conversational response that directly addresses the user's query.
Throughout this process, every interaction is preserved in PostgreSQL, ensuring that subsequent questions can build upon previous exchanges and maintain conversational continuity. The final response appears in the Streamlit interface, completing the cycle and preparing the system for the next user interaction.
5. Getting Started
The repository provides comprehensive setup instructions that guide users through both local development and production deployment scenarios. For developers wanting to experiment and modify the system, local setup allows running all components on a single machine, making it easy to test changes and understand how the components interact.
Production deployment leverages Kubernetes to provide a scalable, reliable system suitable for real-world usage. The setup process includes detailed instructions for configuring each component, managing secrets and environment variables, and establishing proper networking between services.
Essential prerequisites include obtaining an OpenAI API key for accessing the language model and embedding services, setting up a Kubernetes cluster for deployment, and basic familiarity with Docker containers and command-line tools. The system requires several environment variables including OPENAI_API_KEY for the language model, POSTGRES_CONN_STRING for database connectivity, and MINIO_URI with MINIO_ACCESS_TOKEN for vector database access.
6. Advantages of This Architecture
The modular design of this system provides significant advantages for both development and maintenance. Each component can be updated, scaled, or replaced independently without affecting the entire system, making it easier to incorporate new technologies or adapt to changing requirements.
Kubernetes provides inherent scalability that automatically adjusts to usage patterns, ensuring optimal performance during peak periods while controlling costs during lighter usage. The system can handle multiple simultaneous users without degradation, making it suitable for organizational deployment.
Cost-effectiveness comes from using efficient models and intelligent retrieval that only accesses relevant information. Rather than processing entire document collections for every query, the system precisely identifies and retrieves only the most relevant content, minimizing computational overhead and API costs.
The clear separation of concerns makes debugging and troubleshooting straightforward. Issues can typically be isolated to specific components, and the comprehensive logging throughout the system provides visibility into the processing pipeline for optimization and problem resolution.
Summary
This project demonstrates a production-ready approach to building conversational AI systems that seamlessly integrate with existing organizational knowledge. By combining modern AI frameworks, specialized databases, and cloud-native deployment practices, the architecture provides a robust foundation for intelligent applications that can adapt to virtually any domain or use case.
The flexibility of this approach means that organizations can customize the system for their specific needs by simply changing the data sources and adjusting the configuration. Whether building customer support tools, educational platforms, research assistants, or internal knowledge management systems, this foundation provides the scalability, intelligence, and reliability necessary for real-world deployment.
The future of AI applications is increasingly conversational, contextual, and connected to real-world information. This project provides not just a working implementation but a blueprint for understanding how these technologies can be combined effectively. By exploring the code, experimenting with different data sources, and adapting the system to specific requirements, developers and organizations can build AI applications that truly serve their users' needs while leveraging the full potential of modern artificial intelligence technologies.
Resources
- [1] Source code