We will containerize and deploy a MLflow server on a Kubernetes cluster on Google cloud. We will also create the MLflow backend DB, the artifact store and all required service accounts, and secrets on Google cloud. This is achieved by using either gcloud SDK or terraform. The deployment code can be found here.
1. Infrastructure
We will create the following resources in Google cloud:
- Bucket in cloud storage that will be used as artifact storage
- PostreSQL DB in cloud SQL that will be used as mlflow backend db
- Container registry (GCR) that will host our custom mlflow image defined here
- Service account (and json-key) with access to GCS and cloud SQL
- Service account (and json-key) with access to GCR (used by the Google node pool to pull images from GCR)
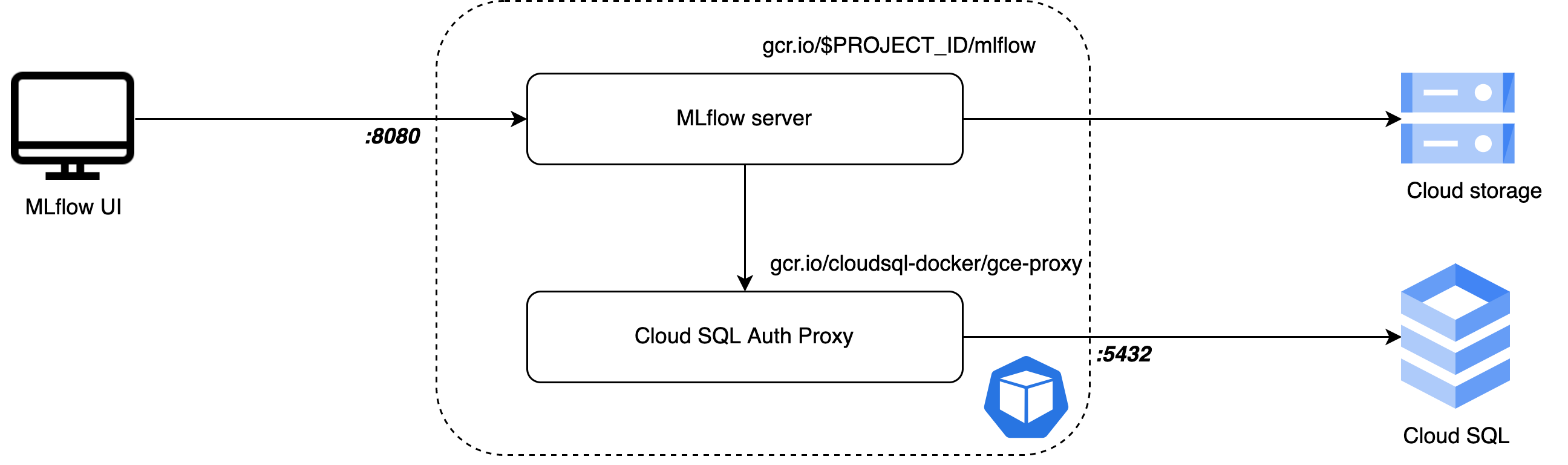
The kubernetes cluster contains:
- Kubernetes Secret that contains credentials of the service account with GCS and SQL access, as well as access to the backend db
- Kuberentes Configmap
- Kubernetes Deployment where each pod holds two containers:
- cloud sql auth proxy container that creates a secure connection to the PostgreSQL DB
- mlflow server that connects to the PostgreSQL DB via the cloud sql auth proxy. We use a custom build image that is defined here.
- Kubernetes Service
2. Deployment with Google cloud SDK
We will rely on the Google cloud SDK to create the resources of interest. To run the commands below you need to have gsutil, gcloud and OpenSSL CLIs installed.
- Setup environment variables:
- Create the required resources in Google cloud (except the kubernetes cluster): Unfortunately, I am not able to create a kubernetes cluster with the gcloud sdk so you have to use the UI to create it.
- Creation of the Kubernetes cluster components. You have to change the kubectl context: There is an option for local deployment with docker-desktop. In this case you have to create a docker-registry secret that porvides access to the container registry with our custom mlflow image: The commands for the creation of the remaining components are the same both for the local and for the Google cloud deployment:
- Test if everything works:
To test if the Mflow server is running you can execute the following python code snippet and verify through the mlflow UI that the results are logged. In the experiment definition you will see that we are using theGCS_CREDENTIALSto store the artifacts in GCS. You also have to change the tracking URI.
3. Deployment with terraform
To understand the following code snippets you should look at the source code provided here.
- Install the terraform version manager. We will work with version 1.2.7:
- Set the
project,regionandzonein./terrafrom/variables.tfand authenticate: The following command will create the required infrastructure (backend db, cloud storage, kubernetes cluster and service accounts). It will also create the namespace mlflow and add to it a config-map and a secret with all relevant credentials for the service. - To deploy the service, we first have to build a mlflow-server image (content in ./mlflow_server directory) and push it to the container registry in our project. We will use Google cloud build. As a result the image
gcr.io/${PROJECT_ID}/mlflow:${TAG_NAME}should be created. - The remaining components that have to be created are described in
kubernetes/mlflow.yaml. We have to change the image of the mlflow-server-container (line 21) to point to the image that we have created in the previous step. We can use kubectl to crete the missing components: